mmx::univariate Namespace Reference
Module for Univariate POLynomials with a Direct Access Representation. More...
Classes
- struct monomials
Functions
- template<class R > int degree (const R &p)
- template<class C > int degree (const monomials< C > &a)
- template<class C > int check_degree (monomials< C > &a)
- template<class C > void add (monomials< C > &r, const monomials< C > &a, const monomials< C > &b)
- template<class C > void add (monomials< C > &r, const monomials< C > &a, const C &c)
- template<class C > void add (monomials< C > &r, const C &c)
- template<class C > void add (monomials< C > &r, const monomials< C > &a)
- template<class C > void sub (monomials< C > &r, const monomials< C > &a, const monomials< C > &b)
- template<class C > void sub (monomials< C > &r, const monomials< C > &a)
- template<class C > void sub (monomials< C > &r, const monomials< C > &a, const C &c)
- template<class C , class X > void sub (monomials< C > &r, const monomials< C > &a, const X &x)
- template<class C > void sub (monomials< C > &r, const C &c)
- template<class C > void mul (monomials< C > &r, const monomials< C > &a, const monomials< C > &b)
- template<class C > void mul (monomials< C > &r, const C &c)
- Multiplication of a polynomial by a monomial or a scalar.
- Multiplication of a polynomial by a monomial or a scalar.
- template<class C > void mul (monomials< C > &a, const monomials< C > &b)
- template<class C > void mul (monomials< C > &r, const monomials< C > &p, const C &c)
- template<class C > void shift (monomials< C > &r, const monomials< C > &p, int d, int v=0)
- template<class C > void div (monomials< C > &r, const monomials< C > &a, const monomials< C > &b)
- template<class C > void div (monomials< C > &r, const monomials< C > &b)
- template<class C > void div (monomials< C > &r, const C &c)
- template<class R > R::value_type lcoeff (const R &p)
- template<class R > R::value_type tcoeff (const R &p)
- template<class OSTREAM , class C > OSTREAM & print_as_coeff (OSTREAM &os, const C &c, bool plus)
- template<class OSTREAM , class C , class VAR > OSTREAM & print (OSTREAM &os, const monomials< C > &p, const VAR &var)
- template<class OSTREAM , class C > OSTREAM & print (OSTREAM &os, const monomials< C > &p)
- template<class R , class C > void set_monomial (R &x, const C &c, unsigned n)
- template<class R , class S > void add_cst (R &r, const S &c)
- template<class R , class S > void sub_cst (R &r, const S &c)
- template<class R > void mul_index (R &r, const R &a, const R &b)
- template<class R > void mul_index_it (R &r, const R &a, const R &b)
- template<class R > void mul (R &a, const R &b)
- template<class R > void mul_index (R &a, const R &b)
- template<class C , class R > C eval_horner (const R &p, const C &c)
- template<class C , class R > C eval_horner_idx (const R &p, const C &c)
- template<class C , class R > C eval (const R &p, const C &c)
- template<class C , class R > C eval_homogeneous (const R &p, const C &a, const C &b)
- template<typename POL , typename X > int sign_at (const POL &p, const X &x)
- template<class R > void div_rem (R &q, R &a, const R &b)
- template<class R > void checkdegree (R &p)
- template<class R > R diff (const R &p)
- template<class R > void reciprocal (R &w, const R &p)
- template<class R > void reverse (R &p, typename R::size_type n)
- template<class R > R::value_type derive (const R p, typename R::value_type x)
- template<class R > void reduce (R &p, const typename R::size_type &e)
- template<class R , class C > void scale (R &t, const R &p, const C &l)
- template<class R > void diff (R &r, const R &p)
- template<class T > void reduce (T &p, const typename T::size_type &e)
- template<class T > void reverse (T &p, int n)
- template<class O , class R , class I > void eval (O &p, O &dp, const R &Pol, const I &x)
- template<class R > R::value_type derive (const R &Pol, const typename R::value_type &x)
- template<class R , class C > void shift (R &p, const C &c)
- template<class R , class C > void shift (R &r, const R &p, const C &x0)
- template<class R , class C > void inv_scale (R &r, const R &p, const C &l)
- template<class T , class P , class C > void convertm2b (T &bz, const P &p, unsigned size, const C &a, const C &b)
- template<class R > void coeff_modulo (R &r, const typename R::value_type &x)
- template<class S , class R > S numer (const R &f)
Detailed Description
Module for Univariate POLynomials with a Direct Access Representation.
It contains generic implementations on univariate (dense) polynomials. This set of functions apply when R provides the following methods or definitions:
typename R::value_type; typename R::size_type; typename R::iterator; typename R::reverse_iterator; iterator_t R::begin(); iterator_t R::end(); value_type R::operator[](int);
Function Documentation
| void mmx::univariate::add | ( | monomials< C > & | r, | |
| const monomials< C > & | a | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 244 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References add(), and check_degree().
00244 { 00245 array::add(r,a); 00246 check_degree(r); 00247 }
| void mmx::univariate::add | ( | monomials< C > & | r, | |
| const C & | c | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 234 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References check_degree(), degree(), and Polynomial.
00234 { 00235 if(degree(r)>-1) { 00236 r[0]+=c; 00237 } 00238 else 00239 r= Polynomial(c,0); 00240 check_degree(r); 00241 }
| void mmx::univariate::add | ( | monomials< C > & | r, | |
| const monomials< C > & | a, | |||
| const C & | c | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 223 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References check_degree(), degree(), and Polynomial.
00223 { 00224 if(degree(a)>-1) { 00225 r=a; r[0]+=c; 00226 } 00227 else 00228 r= Polynomial(c,0); 00229 check_degree(r); 00230 }
| void mmx::univariate::add | ( | monomials< C > & | r, | |
| const monomials< C > & | a, | |||
| const monomials< C > & | b | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 216 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References check_degree().
Referenced by add(), and div_rem().
00216 { 00217 array::add(r,a,b); 00218 check_degree(r); 00219 }
| void mmx::univariate::add_cst | ( | R & | r, | |
| const S & | c | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 429 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
| int mmx::univariate::check_degree | ( | monomials< C > & | a | ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 207 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
Referenced by add(), div(), monomials< C >::monomials(), mul(), and sub().
| void mmx::univariate::checkdegree | ( | R & | p | ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 579 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
Referenced by set_monomial().
| void mmx::univariate::coeff_modulo | ( | R & | r, | |
| const typename R::value_type & | x | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 873 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
| void mmx::univariate::convertm2b | ( | T & | bz, | |
| const P & | p, | |||
| unsigned | size, | |||
| const C & | a, | |||
| const C & | b | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Convert the representation in the monomial basis to the representation in the Bezier basis of $[a,b]$. The matrix of the change of bases is 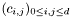 with
with 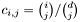 if
if 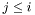 and
and 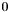 otherwise.
otherwise.
Definition at line 847 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References mmx::assign(), C, scale(), mmx::array::set_cst(), and shift().
00847 { 00848 typedef typename T::value_type coeff_t; 00849 T pps(p.size()); 00850 array::assign(pps,p); 00851 00852 if(a !=0) 00853 shift(pps,pps,a); 00854 00855 scale(pps, pps, C(b-a)); 00856 00857 array::set_cst(bz,pps[0]); 00858 int dn=1, nm=1; 00859 00860 for(unsigned j=1; j<size; j++) { 00861 dn *= (size-j); dn/= j; 00862 nm=1; 00863 bz[j] += pps[j]/dn; 00864 for(unsigned i=j+1; i<size; i++) { 00865 nm *= i; nm/= (i-j); 00866 bz[i] += pps[j]*nm/dn; 00867 } 00868 } 00869 }
| int mmx::univariate::degree | ( | const monomials< C > & | a | ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 201 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
| int mmx::univariate::degree | ( | const R & | p | ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 194 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
Referenced by add(), diff(), div_rem(), eval_homogeneous(), eval_horner(), eval_horner_idx(), lcoeff(), AkritasBound< RT >::lower_bound(), HongBound< RT >::lower_bound(), Cauchy< C >::lower_bound(), NISP< C >::lower_bound(), AkritasBound< RT >::lower_power_2(), Cauchy< C >::lower_power_2(), mmx::min_bound(), mul(), mul_index(), numer(), print(), reciprocal(), shift(), and sub().
| R::value_type mmx::univariate::derive | ( | const R & | Pol, | |
| const typename R::value_type & | x | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Return an evaluation of the derivation of an univariate polynomial for the value 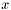 . Example:
. Example:
upoldse<R> p(...);
upoldse<R>::value_type x,d;
d=univariate::derive(p,x);
Definition at line 755 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References eval().
00756 { 00757 typename R::value_type p,res; 00758 eval(p,res,Pol,x); 00759 return res; 00760 };
| R::value_type mmx::univariate::derive | ( | const R | p, | |
| typename R::value_type | x | |||
| ) | [inline] |
| void mmx::univariate::diff | ( | R & | r, | |
| const R & | p | |||
| ) | [inline] |
The derivative of the polynomial p is put in r. r should be allocated wi the correct size.
Definition at line 608 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References degree().
00609 { 00610 int n,i; 00611 r.resize(n=degree(p)); 00612 for( i = 1; i < n+1; ++i) r[i-1] =p[i]*i; 00613 }
| R diff | ( | const R & | p | ) | [inline] |
The derivative of the polynomial p is put in r.
Definition at line 630 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References R.
| void mmx::univariate::div | ( | monomials< C > & | r, | |
| const C & | c | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 349 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References check_degree(), and mmx::array::div_ext().
00349 { 00350 array::div_ext(r,c); 00351 check_degree(r); 00352 }
| void mmx::univariate::div | ( | monomials< C > & | r, | |
| const monomials< C > & | b | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 340 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References check_degree(), div_rem(), and Polynomial.
00340 { 00341 Polynomial tmp(r); 00342 r = Polynomial(0); 00343 div_rem(r,tmp,b); 00344 check_degree(r); 00345 }
| void mmx::univariate::div | ( | monomials< C > & | r, | |
| const monomials< C > & | a, | |||
| const monomials< C > & | b | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 330 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References assert, check_degree(), div_rem(), and Polynomial.
00330 { 00331 assert(&r!=&a); 00332 Polynomial tmp(a); 00333 r = Polynomial(0); 00334 div_rem(r,tmp,b); 00335 check_degree(r); 00336 }
| void mmx::univariate::div_rem | ( | R & | q, | |
| R & | a, | |||
| const R & | b | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Quotient and remainder of a by b. The polynomial a is modified. At the end of the computation, it is equal to the remainder in the euclidean division. The type R should provide a degree function and a direct access operator.
Definition at line 559 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References add(), degree(), mul(), R, and sub().
Referenced by div().
00560 { 00561 typedef typename R::iterator iterator; 00562 int da = degree(a), db=degree(b); 00563 typename R::value_type lb=b[db]; 00564 R t; 00565 q=(R)0; 00566 while (da>=db) { 00567 while(a[da]==0 && da>=db) da--; 00568 if(da>=db) { 00569 R m( a[da]/lb, da-db ); 00570 mul(t,b,m); 00571 t[da]=a[da]; 00572 sub(a,t); 00573 add(q,m); 00574 } 00575 } 00576 }
| void mmx::univariate::eval | ( | O & | p, | |
| O & | dp, | |||
| const R & | Pol, | |||
| const I & | x | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Return an evaluation of the polynomial and its derivative at 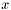 Example:
Example:
upoldse<R> p(...);
upoldse<R>::value_type x,vp,vd;
d=univariate::eval(vp,vd,p,x);
Definition at line 738 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
| C mmx::univariate::eval | ( | const R & | p, | |
| const C & | c | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 520 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References C, and eval_horner().
Referenced by derive().
00521 { 00522 return eval_horner(p,c); 00523 }
| C mmx::univariate::eval_homogeneous | ( | const R & | p, | |
| const C & | a, | |||
| const C & | b | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 526 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References mmx::assign(), C, and degree().
Referenced by mmx::as_interval_data().
00527 { 00528 using namespace let; 00529 C r,y=1,cf; 00530 if(degree(p)>0) { 00531 typedef typename R::const_reverse_iterator const_reverse_iterator; 00532 const_reverse_iterator it=p.rbegin(); 00533 assign(r,*it); it++; 00534 // for(; it !=p.rend(); ++it) {r*=c; assign(cf,*it); r+=cf;} 00535 for(; it !=p.rend(); ++it) {r*=a; y *=b; assign(cf,*it); r=r+cf*y;} 00536 return r; 00537 } else if(degree(p)==0) 00538 { 00539 assign(r,p[0]); return r; 00540 } 00541 else 00542 return C(0); 00543 }
| C mmx::univariate::eval_horner | ( | const R & | p, | |
| const C & | c | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 486 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References mmx::assign(), C, and degree().
Referenced by eval(), and sign_at().
00487 { 00488 using namespace let; 00489 C r,cf; 00490 if(degree(p)>0) { 00491 typedef typename R::const_reverse_iterator const_reverse_iterator; 00492 const_reverse_iterator it=p.rbegin(); 00493 assign(r,*it); it++; 00494 // for(; it !=p.rend(); ++it) {r*=c; assign(cf,*it); r+=cf;} 00495 for(; it !=p.rend(); ++it) {r=r*c; assign(cf,*it); r=r+cf;} 00496 return r; 00497 } else if(degree(p)>-1) 00498 { 00499 assign(r,p[0]); return r; 00500 } 00501 else 00502 return C(0); 00503 }
| C mmx::univariate::eval_horner_idx | ( | const R & | p, | |
| const C & | c | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 506 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
| void mmx::univariate::inv_scale | ( | R & | r, | |
| const R & | p, | |||
| const C & | l | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Scale the variable in the polynomial p by l and put the result r. It computes the coefficients of the polynomial 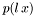 .
.
Definition at line 828 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
Referenced by mmx::inv_scale().
| R::value_type mmx::univariate::lcoeff | ( | const R & | p | ) | [inline] |
Returns the leading coefficient of the polynomial p.
Definition at line 357 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References degree().
Referenced by Cauchy< C >::upper_bound().
00357 { 00358 return p[degree(p)]; 00359 }
| void mmx::univariate::mul | ( | R & | a, | |
| const R & | b | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 463 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References degree(), mul_index(), R, and mmx::array::set_cst().
00464 { 00465 if(degree(a)>=0 && degree(b)>=0) 00466 { 00467 R ta(a); 00468 a.resize(degree(a)+degree(b)+1); 00469 array::set_cst(a,0); 00470 mul_index(a,ta,b); 00471 } 00472 else 00473 array::set_cst(a,0); 00474 }
| void mmx::univariate::mul | ( | monomials< C > & | r, | |
| const monomials< C > & | p, | |||
| const C & | c | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 311 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References check_degree(), and mul().
00311 { 00312 r=p; mul(r,c); check_degree(r); 00313 }
| void mmx::univariate::mul | ( | monomials< C > & | a, | |
| const monomials< C > & | b | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Multiplication of a polynomial by a polynomial;.
Definition at line 306 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References mul(), and Polynomial.
00306 { 00307 Polynomial r; mul(r,a,b); a=r; 00308 }
| void mmx::univariate::mul | ( | monomials< C > & | r, | |
| const C & | c | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Multiplication of a polynomial by a monomial or a scalar.
Definition at line 299 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References mmx::array::mul_ext().
00299 { 00300 array::mul_ext(r,c); 00301 }
| void mmx::univariate::mul | ( | monomials< C > & | r, | |
| const monomials< C > & | a, | |||
| const monomials< C > & | b | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 287 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References assert, C, check_degree(), degree(), mmx::vctops::max(), mul_index(), and mmx::array::set_cst().
Referenced by div_rem(), and mul().
00287 { 00288 assert(&r!=&a); 00289 00290 r.resize(std::max(degree(a)+degree(b)+1,0)); 00291 array::set_cst(r,(C)0); 00292 mul_index(r,a,b); 00293 check_degree(r); 00294 }
| void mmx::univariate::mul_index | ( | R & | a, | |
| const R & | b | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 477 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References degree(), mul_index(), R, and mmx::array::set_cst().
00478 { 00479 R ta(a); 00480 a.resize(degree(a)+degree(b)+1); 00481 array::set_cst(a,0); 00482 mul_index(a,ta,b); 00483 }
| void mmx::univariate::mul_index | ( | R & | r, | |
| const R & | a, | |||
| const R & | b | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 435 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References degree(), and Scalar.
Referenced by mul(), and mul_index().
| void mmx::univariate::mul_index_it | ( | R & | r, | |
| const R & | a, | |||
| const R & | b | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 446 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
00447 { 00448 typename R::const_iterator ia, ib; 00449 typename R::iterator ir, it; 00450 ir=r.begin(); 00451 for (ib=b.begin();ib !=b.end()&& ir != r.end();++ib) { 00452 typename R::value_type c = *ib; 00453 it=ir; 00454 if (c==0) {++ir;continue;} 00455 for (ia=a.begin();ia!=a.end();++ia,++it) { 00456 (*it)+=(*ia)*c; 00457 } 00458 ++ir; 00459 } 00460 }
| S mmx::univariate::numer | ( | const R & | f | ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 878 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References degree(), mmx::denominator(), mmx::lcm(), and mmx::numerator().
00878 { 00879 S p(0,degree(f)); 00880 typename S::value_type d=1; 00881 for(int i=0;i<degree(f)+1;i++) { 00882 if (f[i] !=0) d=lcm(d,denominator(f[i])); 00883 } 00884 for(int i=0;i<degree(f)+1;i++) 00885 p[i]=numerator(f[i])* (d/denominator(f[i])); 00886 return p; 00887 }
| OSTREAM& mmx::univariate::print | ( | OSTREAM & | os, | |
| const monomials< C > & | p | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 412 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References print().
00412 { 00413 return print(os,p, "x"); 00414 }
| OSTREAM& mmx::univariate::print | ( | OSTREAM & | os, | |
| const monomials< C > & | p, | |||
| const VAR & | var | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 376 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References degree(), and print_as_coeff().
Referenced by print().
00377 { 00378 typedef typename Polynomial::value_type coeff_t; 00379 bool plus=false, not_one; 00380 if ( degree(p)<0) 00381 os << coeff_t(0) ; 00382 else { 00383 for(int i= 0; i<=degree(p); i++) 00384 { 00385 if(p[i]!= (coeff_t)0) 00386 { 00387 not_one = (p[i] != (coeff_t)1); 00388 if(not_one || i==0) 00389 print_as_coeff(os,p[i],plus); 00390 plus=true; 00391 // if(i != degree(p) && with_plus_sign(p[i])) os<<"+"; 00392 if(i>0) 00393 { 00394 // if(p[i] == (coeff_t)(-1)) os<<"-"; 00395 // else 00396 if(not_one) 00397 os<<"*"; 00398 os<<"x"; 00399 if(i !=1) 00400 {os<<'^'; os<<i;} 00401 } 00402 // else 00403 // os<<p[0]; 00404 } 00405 } 00406 if(!plus) os << 0 ; 00407 } 00408 return os; 00409 }
| OSTREAM& mmx::univariate::print_as_coeff | ( | OSTREAM & | os, | |
| const C & | c, | |||
| bool | plus | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 367 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
Referenced by print().
| void reciprocal | ( | R & | w, | |
| const R & | p | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Compute the reciprocal of the univariate polynomial 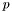 . The result is given in
. The result is given in 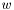 . We assume
. We assume ![$p[0] != 0$](form_8.png) . For this, we consider the equation
. For this, we consider the equation 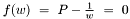 , where
, where 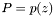 ,
, 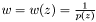 over the ring of formal power series in
over the ring of formal power series in 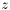 , and apply Newton's iteration to this equation. So we have :
, and apply Newton's iteration to this equation. So we have : 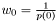 , and
, and 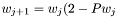 where
where 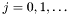 By reducing the different polynomials modulo
By reducing the different polynomials modulo 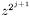 at each step, we have two convolutions of two pairs of vectors of dimensions at most
at each step, we have two convolutions of two pairs of vectors of dimensions at most 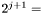 by step.
by step.
Definition at line 660 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References C, degree(), mmx::log(), mmx::pow(), R, and reduce().
00661 { 00662 typedef typename R::size_type size_type; 00663 typedef typename R::value_type C; 00664 00665 const size_type deg = univariate::degree(p)+1; 00666 R w0(deg),v(deg),xp(p); 00667 size_type K = (size_type) (std::log(p.degree()+1)/std::log(2)),j=1; 00668 C p0 = xp[deg-1]; 00669 00670 xp /= p0; 00671 w0 =xp/xp[0]; 00672 v = w0; 00673 v *= C(-1.0); 00674 v[0]+=C(2); 00675 w=v/xp[0]; 00676 w0=w; 00677 while (j <= K) { 00678 univariate::reduce(w0,pow(2,j+1)); 00679 w=xp*w0; 00680 v =w; 00681 v*=C(-1.0); 00682 v[0]+=C(2); 00683 univariate::reduce(v,pow(2,j+1)); 00684 w=w0*v; 00685 w0=w; 00686 j++; 00687 } 00688 univariate::reduce(w,deg); 00689 w/=p0; 00690 }
| void mmx::univariate::reduce | ( | T & | p, | |
| const typename T::size_type & | e | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Truncate an univariate polynomial 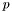 which is modified in output, with a new degree of
which is modified in output, with a new degree of 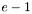 .
.
Definition at line 696 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
| void mmx::univariate::reduce | ( | R & | p, | |
| const typename R::size_type & | e | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Referenced by reciprocal(), and subdivisor< CELL, V >::run().
| void mmx::univariate::reverse | ( | T & | p, | |
| int | n | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Reverse the coefficients of an univariate polynomial, it is performed in place. For a call of this function, the list of arguments must specify, in last, an instance of univariate, the generic type 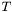 is assumed to be a valid class of univariate polynomial. Example of such a call:
is assumed to be a valid class of univariate polynomial. Example of such a call:
upoldse<...> p(...); univariate::reverse(p,i);
Definition at line 716 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References mmx::sparse::swap().
00717 { for ( int i = 0; i < n/2; i++ ) std::swap(p[i],p[n-i]) ; }
| void mmx::univariate::reverse | ( | R & | p, | |
| typename R::size_type | n | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 590 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References mmx::sparse::swap().
Referenced by mmx::min_bound().
00591 { 00592 int l=n-1; 00593 for(typename R::size_type i=0;i<n/2;i++) 00594 std::swap(p[i],p[l-i]); 00595 }
| void scale | ( | R & | r, | |
| const R & | p, | |||
| const C & | l | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Scale the variable in the polynomial p by l and put the result r. It computes the coefficients of the polynomial 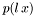 .
.
Definition at line 812 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References C.
Referenced by convertm2b(), and mmx::scale().
00813 { 00814 r=p; 00815 C s(l); 00816 for(unsigned i=1; i< p.size();i++){ 00817 r[i]*=s; 00818 s *=l; 00819 } 00820 }
| void mmx::univariate::set_monomial | ( | R & | x, | |
| const C & | c, | |||
| unsigned | n | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 418 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References checkdegree(), and mmx::array::set_cst().
00419 { 00420 00421 x.resize(n+1); 00422 array::set_cst(x,(typename R::value_type)0); 00423 x[n]=c; 00424 checkdegree(x); 00425 00426 }
| void mmx::univariate::shift | ( | R & | r, | |
| const R & | p, | |||
| const C & | x0 | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Shift the polynomial p at the point x0 and put the result in r. In other words, it computes the coefficients of the polynomial 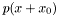 .
.
Definition at line 790 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References shift().
00791 { 00792 r=p; shift(r,x0); 00793 }
| void mmx::univariate::shift | ( | R & | p, | |
| const C & | c | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Inplace shift of the polynomial r at the point x0. It computes the coefficients of the polynomial 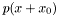 .
.
Definition at line 778 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
| void mmx::univariate::shift | ( | monomials< C > & | r, | |
| const monomials< C > & | p, | |||
| int | d, | |||
| int | v = 0 | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 318 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References degree().
Referenced by convertm2b(), shift(), and mmx::shift().
| int mmx::univariate::sign_at | ( | const POL & | p, | |
| const X & | x | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 547 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References eval_horner(), and mmx::sign().
00548 { 00549 X v= eval_horner(p,x); 00550 return sign(v); 00551 }
| void mmx::univariate::sub | ( | monomials< C > & | r, | |
| const C & | c | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 277 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References check_degree(), degree(), and Polynomial.
00277 { 00278 if(degree(r)>-1) { 00279 r[0]-=c; 00280 } 00281 else 00282 r= Polynomial(-c,0); 00283 check_degree(r); 00284 }
| void mmx::univariate::sub | ( | monomials< C > & | r, | |
| const monomials< C > & | a, | |||
| const X & | x | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 272 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
00272 { 00273 sub(r,a,(C)x); 00274 }
| void mmx::univariate::sub | ( | monomials< C > & | r, | |
| const monomials< C > & | a, | |||
| const C & | c | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 262 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References check_degree(), degree(), and Polynomial.
00262 { 00263 if(degree(a)>-1) { 00264 r=a; r[0]-=c; 00265 } 00266 else 00267 r= Polynomial(-c,0); 00268 check_degree(r); 00269 }
| void mmx::univariate::sub | ( | monomials< C > & | r, | |
| const monomials< C > & | a | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 256 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References check_degree(), and sub().
00256 { 00257 array::sub(r,a); 00258 check_degree(r); 00259 }
| void mmx::univariate::sub | ( | monomials< C > & | r, | |
| const monomials< C > & | a, | |||
| const monomials< C > & | b | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 250 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
References check_degree().
Referenced by div_rem(), and sub().
00250 { 00251 array::sub(r,a,b); 00252 check_degree(r); 00253 }
| void mmx::univariate::sub_cst | ( | R & | r, | |
| const S & | c | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 432 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
| R::value_type mmx::univariate::tcoeff | ( | const R & | p | ) | [inline] |
Return the tail coefficient of the polynomial p.
Definition at line 363 of file vector_monomials.hpp.
 1.6.1
1.6.1